LLMs Hallucinate Links
Frontier LLMs with web access fabricate URLs.
The Problem
I needed to buy 13 components for a DIY robotic arm project. Simple items: cardboard, scissors, hot glue, straws. I asked several frontier LLMs with web search capabilities to find Amazon and Walmart links for each item.
Every model failed. Not partially. Catastrophically.
Results
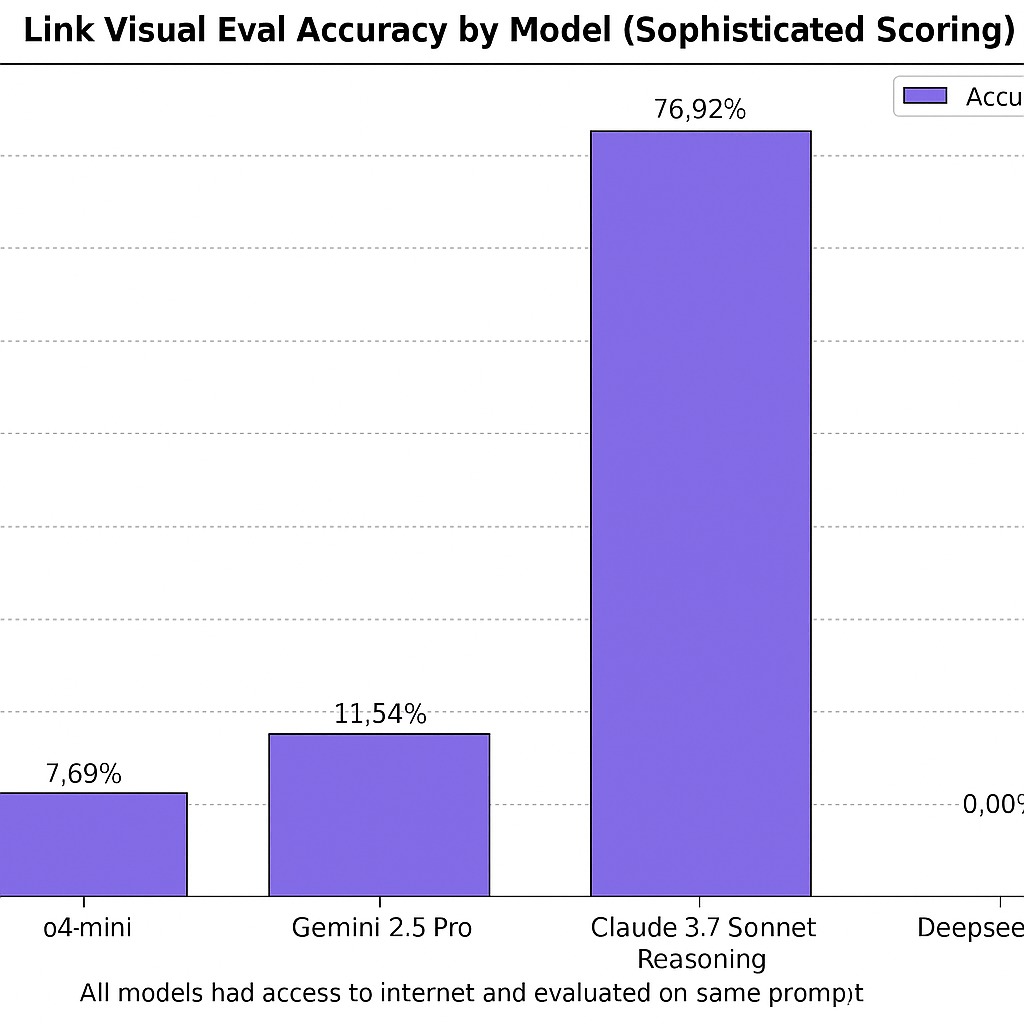
- DeepSeek: 0% accuracy. Every single link was fabricated.
- o4-mini: 7.69% accuracy.
- Gemini 2.5 Pro (with web grounding): 11.54% accuracy.
- Claude 3.7 Sonnet: 76.92% accuracy. The only model approaching usability.
- Shopping/Research: Users waste time clicking dead links
- Legal/Academic: Fabricated citations undermine credibility
- Automation: Any system relying on LLM-generated links will fail silently
All models had internet access. Same prompt. Same products.
The Pattern
The failure mode is consistent: models generate plausible-looking URLs that return 404s or redirect to unrelated products. They do not admit uncertainty. They confidently present broken links as valid results.
This extends beyond shopping. Legal citations show the same pattern:
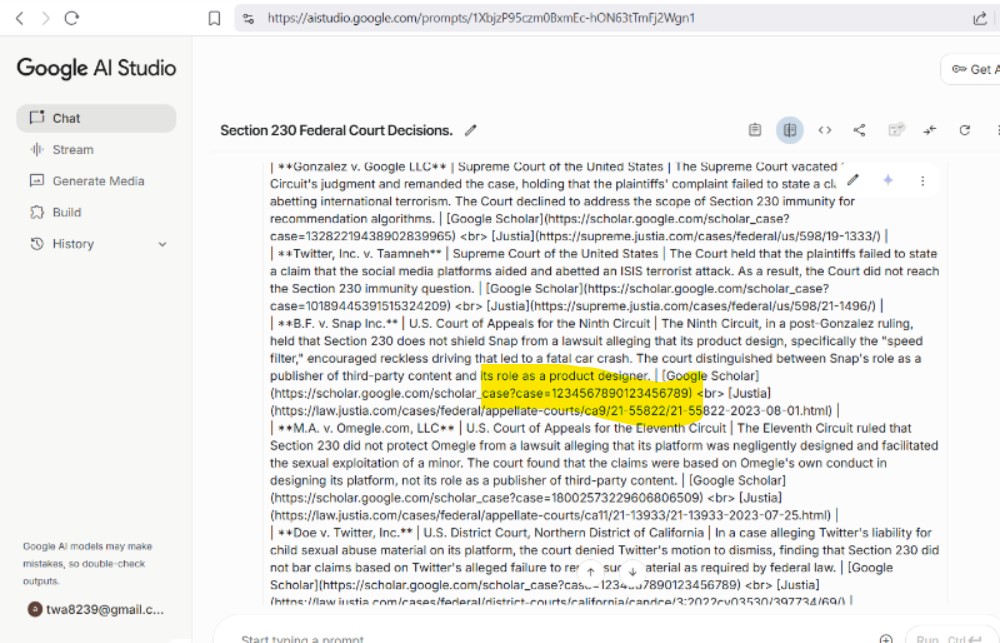
Case numbers like 1234567890123456789 are obvious fabrications. But the surrounding text looks authoritative enough to fool someone who does not verify.
Why This Matters
Takeaway
Never trust an LLM-generated link without verification. The most capable models still hallucinate URLs, and the confidence of their output provides no signal of accuracy.